The Compatible Data Fabric
The Compatible Data Architecture, shown in Figure 1, can best be described as a compatible, modular, analytics-ready data fabric. This Compatible Data Fabric is formed spontaneously from a group of multi-faceted compatible datasets. Each facet of each compatible dataset is a potential join with every other compatible dataset. The Compatible Data Fabric contains many threads that increase data access flexibility.
Disparate data architectures, commonly used today, are composed of incompatible datasets connected by data transformation software that moves and transforms data from one incompatible dataset to another. This data transformation software has been characterized as the data integration hairball because of its complexity. In contrast, the Compatible Data Architecture relies on dynamic on-demand dataset blending using the direct dataset interoperability of the compatible modular datasets. The Compatible Data Architecture is clearly a more innovative, more flexible, and less complex data architecture.
Enriching Your Existing Data Architecture to be Compatible
Amazingly, Compatible Data Architectures are compatible with and noninvasive to existing data architectures. Just as the Data Compatibility Standards enrich existing datasets without modifying structural metadata, data content, or interfering with their related software, enriching your data architecture is also noninvasive. All existing data architecture components continue to function unincumbered by the dataset commonality which adds dynamic dataset interoperability to each of your data architecture components.
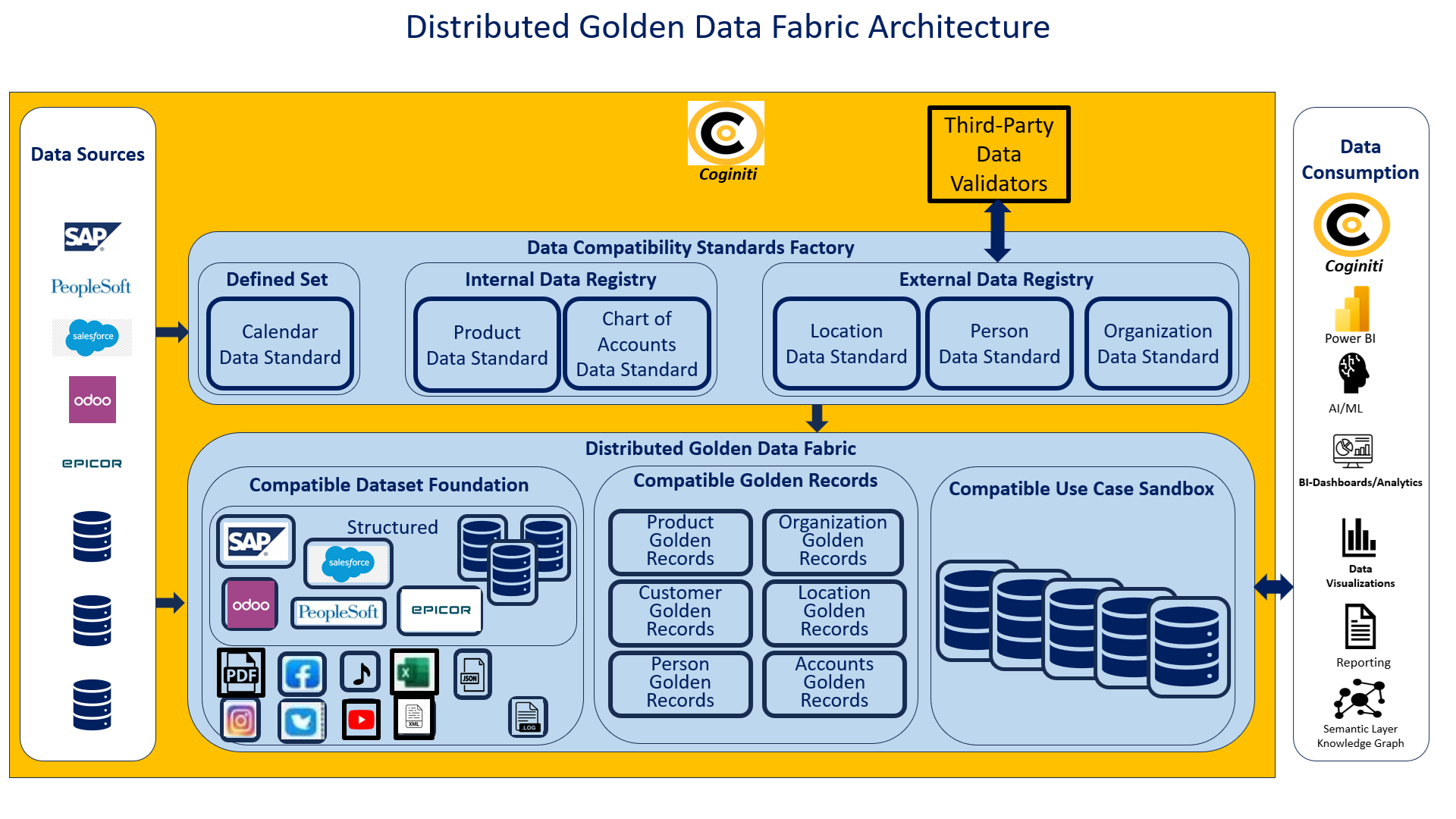
Figure 1: Maxxphase's Best Distributed Data Architecture
The Data Compatibility Standards Factory
As depicted in Figure 1, Data Compatibility Standards are created and maintained in the Data Compatibility Standards Factory. Each standard is specifically designed for a master data domain. Each master data domain instance from each source dataset is uniquely identified and standardized in the factory for use in the distributed data fabric. The main purpose of this section of the data architecture is to enforce data integrity between the compatible datasets of the Distributed Gold Data Fabric, also shown in Figure 1.
The Distributed Golden Data Fabric
The Distributed Golden Data Fabric, shown in Figure 1, contains all compatible datasets. All these compatible datasets are directly interoperable and characterized as analytics-ready, modular, and plug-and-play. As soon as a dataset is enriched to be compatible, it becomes an integral component of the data fabric.
The Compatible Dataset Foundation
This subdivision of the data fabric, shown in Figure 1, contains the most granular structured, semi-structured, and unstructured datasets. These datasets are the foundation of the data fabric. Source datasets that are associated with an operational data system are typically replicated into this subdivision. Other original non-operational datasets can be stored in the compatible dataset foundation as well. All datasets in the foundation are enriched with Data Compatibility Standards from the Data Compatibility Standards Factory.
The Compatible Golden Records
As depicted in Figure 1, this subdivision of the Golden Data Fabric contains compatible master datasets where the business's golden records are maintained. This subdivision of the fabric holds the single source of truth for each data instance of the master data domain. The purpose of the Compatible Golden Records is to provide one location for the data that eliminates data redundancy while greatly improving the data quality of the fabric. Of course, the compatible golden data records can be shared with any other compatible datasets as needed.
The Compatible Use Case Sandbox
Data Compatibility is beneficial to information building, which would occur in the Compatible Use Case Sandbox as depicted in Figure 1. Any subset of data combined, derived, and aggregated from the Compatible Dataset Foundation datasets can be materialized into a compatible dataset for a more focused business use, such as KPI dashboards, periodic reporting, compatible data warehouse, and, of course, AI/ML. Since each compatible dataset supports data warehouse functionality, derived, aggregated, and historical data may enrich each modular plug-and-play dataset. In addition, direct dataset interoperability may be used to blend multiple compatible datasets to materialize a new, consolidated, compatible dataset for repeated detailed data analysis. This form of information building is extremely efficient compared to traditional data transformation and incompatible dataset consolidation methods.
The Business Perspective
Never before has a business had such informational power at their fingertips. The Compatible Data Fabric provides a single source of consistent and trusted instantly available data. Within the data fabric, each compatible dataset forms direct links with every other compatible dataset. These dataset links are the weave of your Compatible Data Fabric. All your data fits together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle, providing a 360ᴼ view of all your data.
The Compatible Data Fabric also supports all the functionality and power of a data warehouse. This embedded data warehouse functionality is an enormous advantage over the conventional data fabric that is merely a data source for constructing a data warehouse. Business intelligence and analytics are intrinsic to your Compatible Data Fabric.

The Technical Perspective
Maxxphase implements compatible datasets in a multi-dimensional form, where each Data Compatibility Standard supports a standardized hierarchy of its master data domain. Each level of granularity for every Data Compatible Standard enforces direct data interoperability between compatible datasets. Each compatible dataset becomes an integral component in a multi-tiered Compatible Data Fabric. The data weaves between compatible datasets are very comprehensive. As such, the Compatible Data Fabric formed from these modular plug-and-play datasets also directly supports multi-dimensional analytics.
Each compatible dataset incorporates all data warehouse functionality, such as roll-ups and drill-downs, slicing, and dicing. You can dynamically blend various combinations of compatible datasets, forming a virtualized or a materialized compatible dataset specific to an analytic need.
Traditional data fabrics tend to have several performance issues. In contrast, compatible datasets are very agile and support data retrieval performance enhancements. The direct data weaves of the Compatible Data Fabric are far more efficient than the indirect, transformed data weaves used in traditional data fabrics. Compatible datasets also support the materialization of aggregate data and consolidated data to eliminate inefficient data retrieval. Compatible Data Fabrics will easily outperform traditional data fabrics.
Compatible datasets fit together with data blending because the data content in compatible datasets have extensive direct dataset interoperability. The resulting Compatible Data Fabric has all the functionality of a traditional data fabric and a whole lot more. If you have an interest in data fabrics, you need to find out about Compatible Data Fabrics.
